
-
BIOTAB7 KILLS ALL MOLD
When it comes to mold, there’s no time to waste. Only time to kill.
Treat mold in minutes in homes, offices, gardens and even boats.
Biotab7 : disinfectant fungicide that kills all mold.
HOW TO USE BIOTAB7 FOR MOLD REMEDIATION
-
1. PRE-CLEAN
Remove gross soils and surface mold build-up.
-
2. MIX
Add five x 1 gram tablets to a 1 quart spray bottle and fill with water. This will give you a powerful solution of 500 PPM.
-
3. SPRAY
Spray liberally, misting occasionally. Biotab7 will eliminate surface mold, chase the microbes buried within the substrate, and kill airborne spores.
-
4. DONE
Watch the mold disappear within 5 minutes. Wipe away residue and muck. For extra protection, leave an open container of Biotab7 to kill airborne spores.
BEFORE AND AFTER BIOTAB7
-
KILLS ALL MOLDS
HOMES, OFFICES, HOTELS
- Stachybotrys (black mold)
- Aspergillus (common in American homes)
- Cladosporium (respiratory risk)
- Alternaria (most common allergenic mold in the world)
- Penicillin (water damage)
HORTICULTURE
- Botrytis (root rot)
- Powdery Mildew (onions, wheat, cannabis)
- S. sclerotiorum (white mold, on vegetables, tomatoes, trees)
-
DANGERS OF MOLD
Black mold is a neurotoxin, triggering headaches and brain fog. While it’s well known that mold triggers asthma and respiratory illness, some molds produce mycotoxins that lead to chronic health problems in humans and animals.
WHY YOU NEED BIOTAB7
Dead mold spores are just as harmful as live ones, so you need a fungicide like Biotab7 that is specifically designed to kill the organism - not just a general cleaner.
A musty odor is a telltale sign of mold: the mold is releasing microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) into the air.
PREVENTING MOLD
Prevent mold by keeping the environment dry and clean.
STAYING DRY
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends maintaining a relative humidity between 30% to 50% to prevent mold growth. You can measure this with a hygrometer: an affordable tool ($10-$50) found at most hardware stores. If your reading is above 45% humidity, it’s time to act.
- Ensure adequate ventilation in kitchens, bathrooms, and wet areas
- Use dehumidifiers
- Maintain HVAC units
- Maintain air filters
- Check for plumbing leaks
- Use Biotab7 to clean at-risk surfaces
KEEP IT CLEAN
Mold thrives in cluttered spaces where dampness forms. Whilst it grows on common building materials, it can also feed on cockroach and dust mite feces, skin flakes, and food particles. Utilizing a strong and safe biocide like Biotab7 destroys these potential growth mediums, stopping mold before it can start.
MOLD COLONY GROWTH RATES
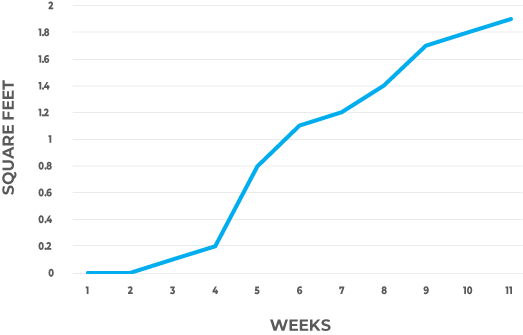
This data comes from the study Controlled Study of Mold Growth by Krause, Geer, Swenson, Fallah, & Robbins (2006), available here.
Mold establishes itself slowly for the first few weeks, before exploding into a rapid growth cycle at approximately 4 weeks.
Spores present were stachybotrys (black mold), penicillium, cladosporium, and acremonium. "Nearly confluent colonization" occured - meaning small spore growths started in patches, but quickly merged into large colonies.
At the end of the 10 week study, the colonies spanned two square feet.
WELCOME TO ABT
We are a passionate team of experienced professionals and scientists, creating new standards in disinfection.
Biotab7 is a revolutionary biocide that utilizes the latest advancements in chemistry. The result? A truly versatile chemical that is 18 products in 1.
INDUSTRIES
CONTACT
- 523 Sawgrass Corporate Parkway, Sunrise, FL 33325, USA


